Bivalvia |
Adapedonta |
Solenidae
Environment: milieu / climate zone / गहराई सीमा / distribution range
पारिस्थितिकी
. Tropical
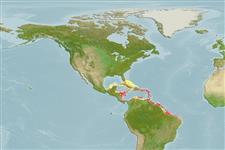
Western Atlantic: Caribbean to Brazil.
Length at first maturity / आकार / Weight / Age
परिपक्व अवधि: Lm ? range ? - ? cmCommon length : 9.6 cm TL पुल्लिंग / अलिंग; (संदर्भ 344)
Shell very elongate (ratio length: width 5:1), dorsal and ventral margins parallel, hinge posterior, with single pair of cardinal teeth. Shell thicker at anterior margin. Umbones at the angle formed by dorsal and posterior margins. Colour: brown to purple.
Infaunal in muddy sand, in intertidal or shallow subtidal depths (Ref. 344).
Life cycle and mating behavior
परिपक्व अवधि | पुनरुत्पत्ति | मछलीऔ का अंडे देना | Eggs | Fecundity | Larvae
Members of the class Bivalvia are mostly gonochoric, some are protandric hermaphrodites. Life cycle: Embryos develop into free-swimming trocophore larvae, succeeded by the bivalve veliger, resembling a miniature clam.
Leal, J.H. 2003 Bivalves. p. 25-98. In Carpenter, K.E. (ed.). The living marine resources of the Western Central Atlantic. Volume 1: Introduction, molluscs, crustaceans, hagfishes, sharks, batoid fishes, and chimaeras. FAO Species Identification Guide for Fishery Purposes and American Society of Ichthyologists and Herpetologists Special Publication No. 5. 1600p. (संदर्भ 344)
IUCN Red List Status
(संदर्भ 130435: Version 2025-1)
CITES status (संदर्भ 108899)
Not Evaluated
CMS (संदर्भ 116361)
Not Evaluated
Threat to humans
Human uses
मात्स्यिकी: व्यापारिक
| FishSource |
साधन
अधिक जानकारी
Trophic EcologyFood items (preys)
संघटक आहार
आहार खपत
परभक्षी
Population dynamicsबाढ़
Max. ages / sizes
Length-weight rel.
Length-length rel.
Length-frequencies
Mass conversion
बहुतायत
Life cycleपुनरुत्पत्तिपरिपक्व अवधिFecundityमछलीऔ का अंडे देनाEggsEgg developmentLarvae PhysiologyOxygen consumption
Human RelatedStamps, coins, misc.
इंटरनेट स्रोत
Estimates based on models