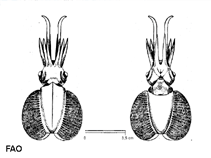
Chtenopteryx sicula (Verany, 1851)
Sicilian comb-finned squid| Native range | All suitable habitat | Point map | Year 2050 |

|
| This map was computer-generated and has not yet been reviewed. |
| Chtenopteryx sicula AquaMaps Data sources: GBIF OBIS |
Classification / Names Κοινά ονόματα | Συνώνυμα | CoL | ITIS | WoRMS
Cephalopoda | Bathyteuthida | Chtenopterygidae
Environment: milieu / climate zone / εύρος βάθους / distribution range Οικολογία
βαθυπελαγικό(ς); εύρος βάθους 200 - 1000 m (Αναφ. 843). Tropical
Distribution Χώρες | Περιοχές FAO | Οικοσυστήματα | Παρουσίες | Εισαγωγές
Cosmopolitan, tropical and subtropical waters.
Length at first maturity / Μέγεθος / Weight / Age
Γεννητική Ωρίμανση: Lm ? range ? - ? cm Max length : 11.5 cm ML αρσενικό/απροσδιόριστο; (Αναφ. 104052)
Life cycle and mating behavior Γεννητική Ωρίμανση | Αναπαραγωγή | Γεννοβολία | Eggs | Γονιμότητα | Larvae
Main reference
Αναφορές | Συντονιστής | Συνεργάτες
Turgeon, D.D., J.F. Quinn Jr., A.E. Bogan, E.V. Coan, F.G. Hochberg, W.G. Lyons, P.M. Mikkelsen, R.J. Neves, C.F.E. Roper, G. Rosenberg, B. Roth, A. Scheltema, F.G. Thompson, M. Vecchione and J.D. Willams 1998 Common and scientific names of aquatic invertebrates from the United States and Canada: Mollusks, 2nd ed. American Fisheries Society (Special publication 26), Bethesda, Maryland. 526 p. (Αναφ. 1667)
IUCN Red List Status
(Αναφ. 130435: Version 2025-1)
CITES status (Αναφ. 108899)
CMS (Αναφ. 116361)
Threat to humans
Human uses
| FishSource |
Εργαλεία
Περισσότερες πληροφορίες
Διαδικτυακές πηγές
BHL | BOLD Systems | CISTI | DiscoverLife | FAO(Publication : search) | Fishipedia | GenBank (genome, nucleotide) | GloBI | Gomexsi | Google Books | Google Scholar | Google | PubMed | Δέντρο Ζωής | Wikipedia (Go, αναζήτηση) | Zoological Record