Malacostraca |
Stomatopoda |
Lysiosquillidae
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Ecology
Benthic; depth range 0 - 30 m (Ref. 436). Tropical
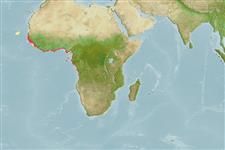
Off West Africa, from the Cape Verde Islands; Senegal to Angola.
Length at first maturity / Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm ? range ? - ? cm Max length : 27.0 cm BL male/unsexed; (Ref. 417); common length : 20.0 cm BL male/unsexed; (Ref. 436)
A moderately large to very large stomatopod. Body conspicuously flattened, smooth, lacking ridges or spines except for the tail region; 6th abdominal segment and telson; which is prickly with small bumps or tubercles. Telson with a raised, elongate boss medially, but without a median ridge. Rostral plate broader than long, with a low median crest on its anterior third. Claws very large, often longer than carapace and armed with 10 to 12 sharp spines on the terminal segment. Color: marked with light and dark cross bands (Ref. 436).
Found in shallow water (Ref. 436).
Life cycle and mating behavior
Maturity | Reproduction | Spawning | Eggs | Fecundity | Larvae
Some members of the order Stomatopoda pair for life and some come together only to mate. Males produce sperm ducts rather than spermatophores; females can brood a maximum of 50,000 eggs. Life cycle: Eggs hatch to a planktonic zoea which lasts for 3 months.
Schneider, W. 1990 FAO species identification sheets for fishery purposes. Field guide to the commercial marine resources of the Gulf of Guinea. Prepared and published with the support of the FAO Regional Office for Africa. Rome: FAO. 268 p. (Ref. 417)
IUCN Red List Status
(Ref. 130435: Version 2025-1)
CITES status (Ref. 108899)
Not Evaluated
Not Evaluated
Threat to humans
Harmless
Human uses
| FishSource |
Tools
More information
Trophic EcologyFood items (preys)
Diet composition
Food consumption
Predators
Population dynamicsGrowthMax. ages / sizesLength-weight rel.Length-length rel.Length-frequenciesMass conversionAbundance Life cycleReproductionMaturityFecunditySpawningEggsEgg developmentLarvae PhysiologyOxygen consumption
Human RelatedStamps, coins, misc.
Internet sources
Estimates based on models
Fishing Vulnerability
Low vulnerability (17 of 100).
Price category
Unknown.